Developing and debugging frontends
The mephisto-core package
We provide the mephisto-core package for use in your front-end React tasks.
The mephisto-core project surfaces three React hooks depending on your use case:
useMephistoTask- Used for static tasks where one-time initial data is enough to power the task. See the example task in/examples/static_react_task/for an example project using this hook.useMephistoLiveTask- Used for multi-turn, socket-based tasks, such as a dialogue task. See the example task in/examples/parlai_chat_task_demo/for an example project using this hook.useMephistoRemoteProcedureTask- Used for static tasks that require access to some remote function on the back-end, for example invoking a back-end model for model-assisted annotation. See the example task in/examples/remote_procedure/mnist/for an example project using this hook.
Complete documentation for each of the hooks can be found in the associated README for the mephisto-core package.
Reusable UI component libraries
@annotated [BETA]
To make common annotation tasks easier, we provide the @annotated/* suite of packages.
These suite of packages were formerly published under the annotation-toolkit and have now been broken down into their own individual packages. We provide helper UI components such as @annotated/bbox, @annotated/video-player, etc.
We welcome contributions to these packages. To create your own package, you can clone the template folder at packages/annotated/__template__.
bootstrap-chat
For chat-based components, we provide custom UI components in the bootstrap-chat package. You can find further information for them in the associated README for the bootstrap-chat package.
Adding UI error handling to tasks
Currently, we have beta functionality for error handling. We provide a few ways of getting a signal into how your tasks are faring:
- Auto-logging errors for React-based tasks
- Proactively alerting crowd workers when an error occurs and encouraging them to contact you if this happens
- Exposing error logging infrastructure for more advanced custom front-end use cases
Automatic frontend logging
For #1 above, auto-logging can be enabled for React apps by importing the <ErrorBoundary /> component and wiring it up as such:
import { ErrorBoundary } from "mephisto-core";
...
const { handleFatalError, /* ... */ } = useMephistoTask();
...
return (
<ErrorBoundary handleError={handleFatalError}>
<MyApp />
</ErrorBoundary>
);
This will automatically send an error packet to the backend Mephisto server when an error occurs.
Alerting crowd-workers of issues
To opt into #2 above, you need to define a global variable as such:
window._MEPHISTO_CONFIG_ = {
/* required: */
ADD_ERROR_HANDLING: true,
/* optional: */
ERROR_REPORT_TO_EMAIL: "[email protected]"
}
This will show a prompt as such if an uncaught error is detected:
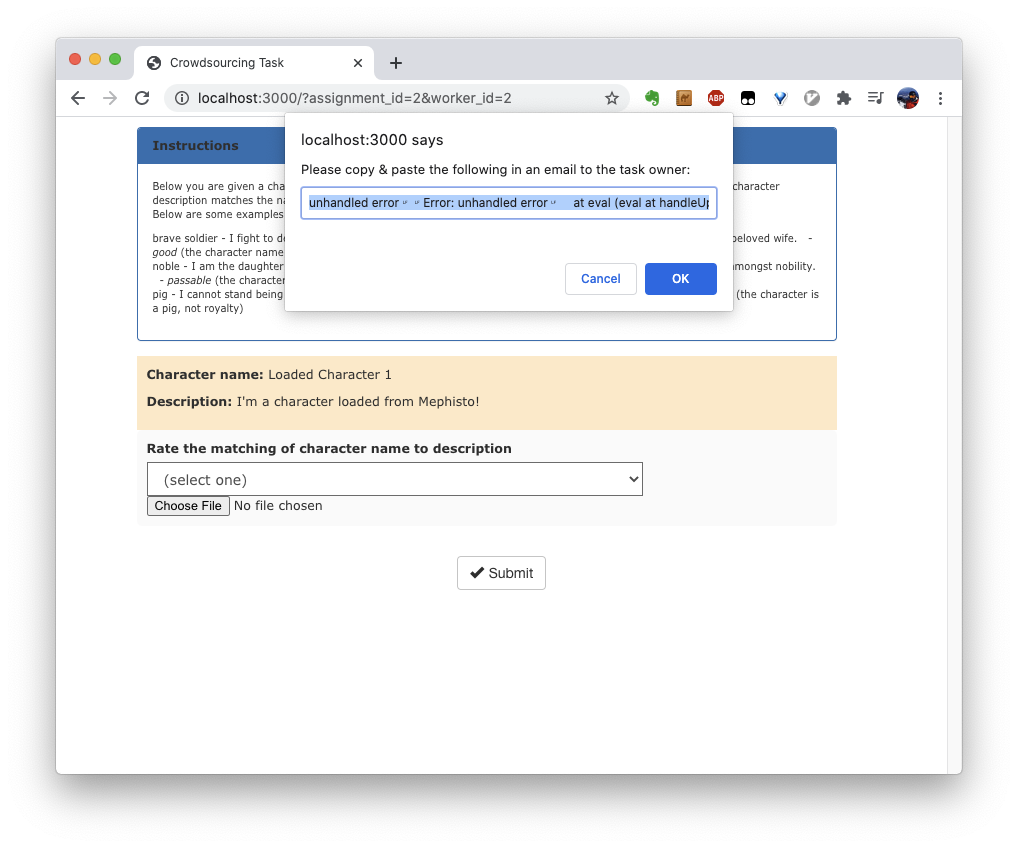
Advanced Usage
handleFatalError can also be used in any custom logic code you wish - for example, in handling errors for AJAX requests which live outside of the scope of React Error Boundaries:
fetch("example.org/api/endpoint")
.catch(err => handleFatalError(err.toString()));